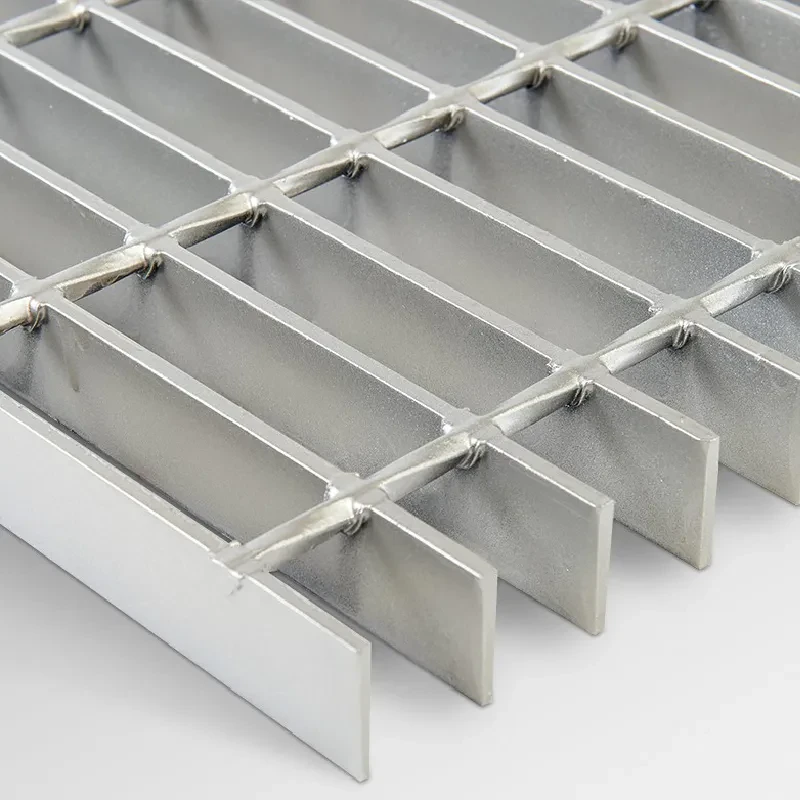
The hot dip galvanization process begins by cleaning the steel to remove any contaminants, such as rust, oil, or dirt. After cleaning, the steel is submerged in a bath of molten zinc at approximately 450°C (842°F). The zinc reacts with the iron in the steel to form a series of zinc-iron alloy layers, which are then topped with a corrosion-resistant zinc layer. This method not only provides a tough, protective coat but also ensures a strong bond between the coating and the steel, resulting in a longer lifespan.
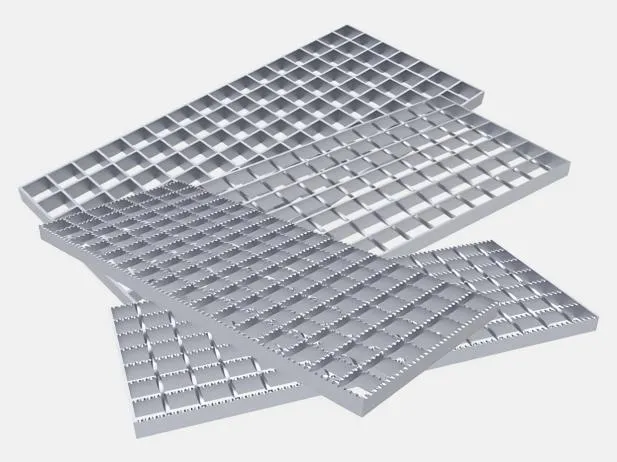
In conclusion, understanding the various sizes and types of steel grating is essential for making informed decisions in construction and industrial applications. Properly sized steel grating can enhance safety, improve functionality, and bring aesthetic value to any project. As industries continue to evolve and demand more innovative solutions, the adaptability and reliability of steel grating remain paramount. Always consult with a professional to choose the right dimensions and style that best meet your specific requirements. By doing so, you can ensure that your project stands the test of time, efficiency, and safety standards.
Steel grating is an essential material used in various industrial, commercial, and architectural applications. Its versatility and strength make it an ideal choice for constructing walkways, platforms, and stair treads. One crucial aspect of steel grating that significantly influences its performance and longevity is its thickness. Understanding this factor is vital for engineers, architects, and project managers involved in the design and construction of steel structures.