Oil seals applications
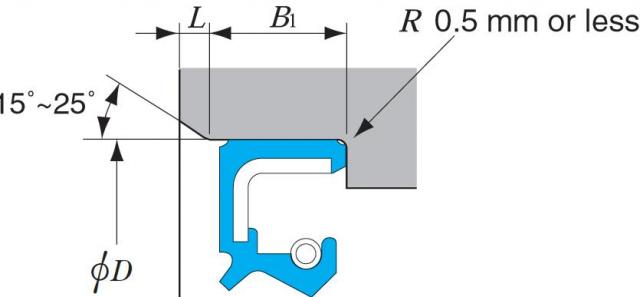
A typical oil seal consists of three common parts: an outer ring, the sealing element, and a spring. The exterior metal ring component provides strength and rigidity to the oil seal in the bore or recessed groove. Attached to that ring is the sealing element. This flexible interior component of the oil seal, the O-ring, prevents any fluid leaks between the shaft and housing. A spring ensures the constant pressure that deforms the O-ring, creating a reliable seal while maintaining radial force on the shaft.
Oil seal characteristics
Leather is probably the oldest of the lip materials still in common use, but the move towards mass production methods has seen a massive increase in the development of synthetic rubbers which lend themselves to accurate and repeatable injection and compression moulding. Nitrile (NBR) is still by far the most common elastomer for “normal” use, whilst Viton® (FKM/FPM) is rapidly replacing Polyacrylate (ACM) and Silicone (VMQ) for high-temperature applications. Viton® also has high resistance to abrasion and chemical attack making it a preferred elastomer. Recent developments in the use of PTFE for Rotary shaft seals has caused widespread interest particularly for high-speed shaft rotation or poor lubrication applications.
The pulley may slide off easily; if not, use a universal puller, which you may be able to hire.


 This is particularly important in the context of today's increasingly stringent environmental regulations, which place a premium on vehicles and machinery that produce minimal pollution This is particularly important in the context of today's increasingly stringent environmental regulations, which place a premium on vehicles and machinery that produce minimal pollution
This is particularly important in the context of today's increasingly stringent environmental regulations, which place a premium on vehicles and machinery that produce minimal pollution This is particularly important in the context of today's increasingly stringent environmental regulations, which place a premium on vehicles and machinery that produce minimal pollution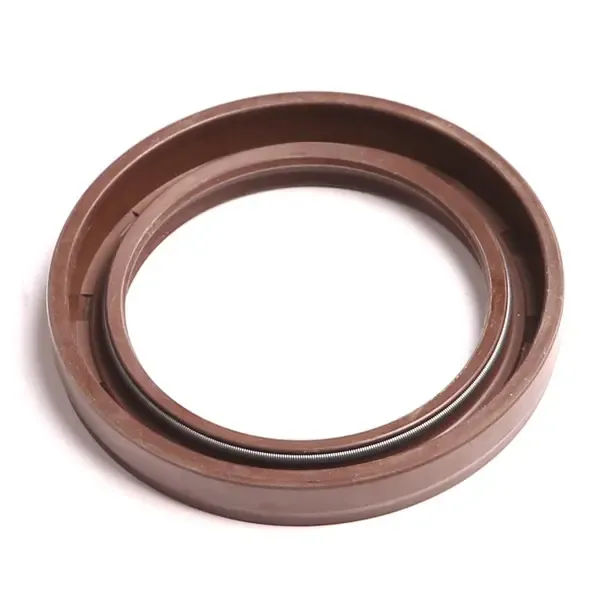 These seals are designed to maintain their integrity even when subjected to significant pressure differences, ensuring that oil remains confined within the system These seals are designed to maintain their integrity even when subjected to significant pressure differences, ensuring that oil remains confined within the system
These seals are designed to maintain their integrity even when subjected to significant pressure differences, ensuring that oil remains confined within the system These seals are designed to maintain their integrity even when subjected to significant pressure differences, ensuring that oil remains confined within the system